Total Knee Replacement
Summary
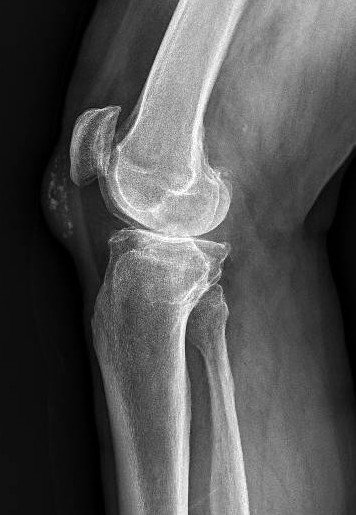
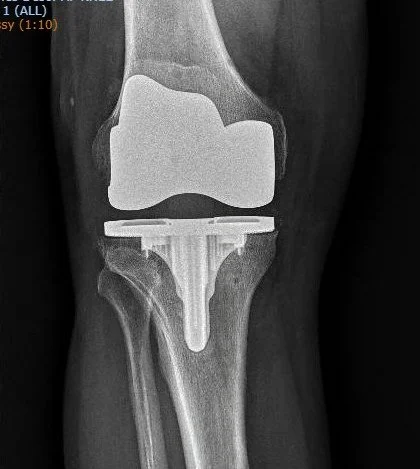
Total knee replacement (total knee arthroplasty) is a surgical procedure that replaces a damaged knee joint with an artificial one. This can significantly improve pain, function, and quality of life for people with severe arthritis or other knee conditions.
Benefits
Pain relief: Significant reduction in knee pain.
Improved function: Increased ability to walk, climb stairs, and perform daily activities.
Improved quality of life: Enhanced overall well-being and ability to participate in activities.
Recovery
Same Day Discharge: Many patients are discharged the same day as surgery
Walking immediately: Will begin walking with walker immediately after surgery
Physical Therapy: Most patients are ambulating with no assistive device by 3 weeks postoperatively and no additional therapy is needed after this
Full Recovery: Fully healed from surgery 10-12 weeks post op but most patients have returned to work before that depending on type of job
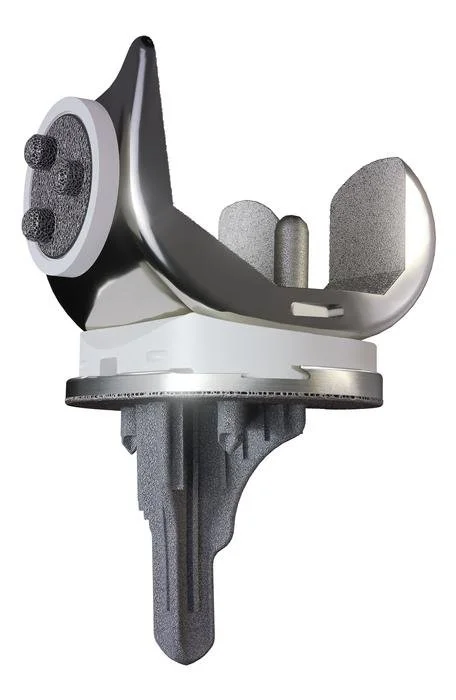
Robotic TKA
Dr. Ratner uses robotic technology for all of his knee replacements. Robotic total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an advanced surgical technique that uses robotic technology to assist surgeons in performing knee replacement surgery with greater precision and personalization
Summary:
Robotic TKA involves the use of a robotic arm or system guided by preoperative imaging (like CT scans) and real-time intraoperative data. The surgeon plans the procedure using 3D models of the patient’s knee, allowing for customized implant positioning and alignment tailored to the individual’s anatomy. During surgery, the robot provides feedback and assists with bone cuts, ensuring accuracy within millimeters, while the surgeon retains full control.
Benefits Compared to Traditional TKA:
Improved Precision and Accuracy
Robotic systems enhance the precision of bone cuts and implant placement, aligning the prosthetic components more accurately with the patient’s unique anatomy. Traditional TKA relies heavily on manual tools and surgeon experience, which can lead to slight variations.
Personalized Surgical Planning
Preoperative 3D modeling in robotic TKA allows for a tailored approach, optimizing implant fit and joint balance. Traditional methods use standard templates and intraoperative adjustments, which may not account for individual variations as effectively.
Reduced Soft Tissue Damage
The robotic assistance minimizes unnecessary exposure and trauma to surrounding tissues, as cuts are more controlled. In traditional TKA, manual techniques may involve more soft tissue disruption.
Potentially Faster Recovery
Studies suggest that the precision and reduced tissue damage in robotic TKA can lead to quicker rehabilitation and less postoperative pain for some patients compared to traditional methods, though recovery varies by individual.
Better Long-Term Outcomes
Accurate alignment may improve the longevity of the implant by reducing wear and the risk of loosening. Traditional TKA, while effective, has a higher chance of suboptimal alignment, potentially affecting durability.
Consistency Across Procedures
Robotic systems offer reproducible results, reducing variability seen in traditional TKA, where outcomes can depend more on the surgeon’s skill and experience.